TREATMENT OF ANEURYSM AND STROKE
Treatment Of Aneurysm And Stroke
Brain Aneurysm
An intracranial aneurysm, also known as a brain aneurysm, is a cerebrovascular disorder in which weakness in the wall of a cerebral artery or vein causes a localized dilation or ballooning of the blood vessel.
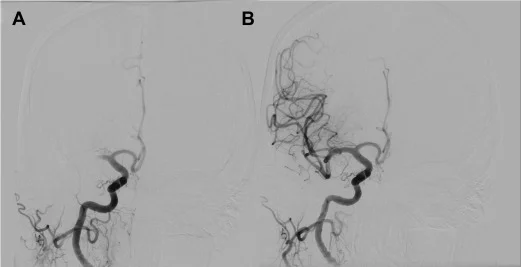
Aneurysms in the posterior circulation (basilar artery, vertebral arteries and posterior communicating artery) have a higher risk of rupture. Basilar artery aneurysms represent only 3–5% of all intracranial aneurysms but are the most common aneurysms in the posterior circulation.
Signs and Symptoms
A small, unchanging aneurysm will produce few, if any, symptoms. Before a larger aneurysm ruptures, the individual may experience such symptoms as a sudden and unusually severe headache, nausea, vision impairment, vomiting, and loss of consciousness, or no symptoms at all.
Treatment
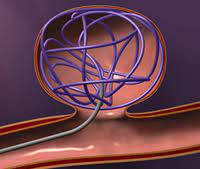
Emergency treatment for individuals with a ruptured cerebral aneurysm generally includes restoring deteriorating respiration and reducing intracranial pressure. Currently there are two treatment options for securing intracranial aneurysms: surgical clipping or endovascular coiling. If possible, either surgical clipping or endovascular coiling is typically performed within the first 24 hours after bleeding to occlude the ruptured aneurysm and reduce the risk of recurrent hemorrhage.


Stroke / Paralysis
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functioning properly. Signs and symptoms of a stroke may include an inability to move or feel on one side of the body, problems understanding or speaking, dizziness, or loss of vision to one side. Signs and symptoms often appear soon after the stroke has occurred. If symptoms last less than one or two hours, the stroke is a transient ischemic attack (TIA), also called a mini-stroke. A hemorrhagic stroke may also be associated with a severe headache.
Management
Ischemic stroke
Aspirin reduces the overall risk of recurrence by 13% with greater benefit early on. Definitive therapy within the first few hours is aimed at removing the blockage by breaking the clot down (thrombolysis), or by removing it mechanically (thrombectomy). The philosophical premise underlying the importance of rapid stroke intervention was summed up as Time is Brain! in the early 1990s. Years later, that same idea, that rapid cerebral blood flow restoration results in fewer brain cells dying, has been proved and quantified.
Endovascular Treatment
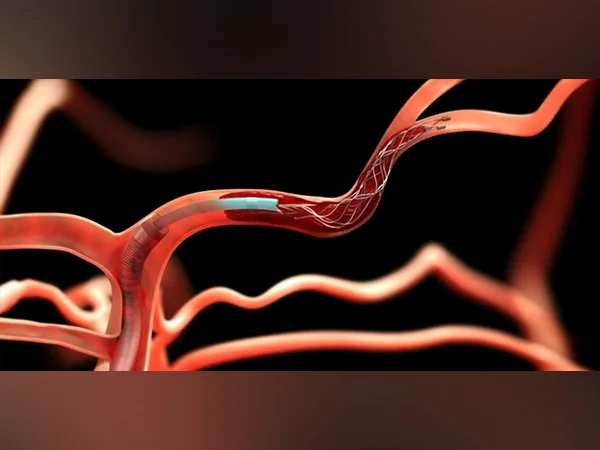
Mechanical removal of the blood clot causing the ischemic stroke, called mechanical thrombectomy, is a potential treatment for occlusion of a large artery, such as the middle cerebral artery.
Mechanical thrombectomy is most effective when done within 6 hours of onset of symptoms. That is why it is important to reach hospital as early as possible.
Book Appointment
-
Varicose Veins & Varicose Ulcer Treatment
-
Non-Healing Wound Management
-
Vascular Malformations
-
Uterine Fibroid or Prostate Embolization
-
Cancer Treatments – TACE, RFA, Embolization
-
Dialysis Access Catherization
-
Diagnostic Procedures – FNAC, Biopsy, Diagnostic Angiography
-
Abscess Treatment - Aspiration, Pigtail Drainage
-
Treatment of Aneurysm and Stroke
-
Other USG, CT & DSA Guided Interventions
