DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT)
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
Is formation of blood clots within veins because of which veins get blocked.It is commonly seen in legs although can occur in arms as well.Patient can present with sudden pain, swelling, redness of legs or arm.
Pulmonary Embolism (PE) is serious complication of DVT where blood clots dislodge from legs towards heart and then veins in lungs.
Delayed complications of DVT are together called as post-thrombotic syndrome, which include skin changes, recurrent swelling, ulcers and secondary varicose veins.
DVT occurs because of decreased blood flow, increased tendency to clot, changes to the blood vessel wall, and inflammation.
Common risk factors for DVT include recent surgery, in older age, active cancer, obesity, infection, inflammatory diseases, antiphospholipid syndrome, trauma, injuries, lack of movement, hormonal birth control, pregnancy, and the period following birth.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is primarily done by simple non-invasive test that is color Doppler also called as color sonography of legs or arm.
In some situation to check abdominal veins or internal cause compressing veins CT /MR/DSA Venography is done
Management
DVT treatment is simple if identified on time and medicines started promptly.
Initially blood thinner injections or oral tablets are given. Adjuvant treatment includes leg elevation , MgSo4 dressing, good hydration and stockings.
If this conservative treatment fails active endovascular intervention is advisable.
Endovascular Treatment.
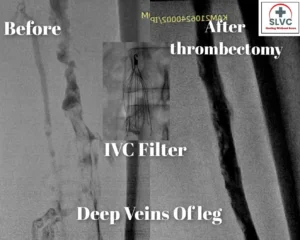
Thrombolysis – Is injecting blood clot dissolving medicines within clot via small pipes having multiple holes in it.
Mechanical thrombectomy is removing blood clots by pipes by suction and many other newer mechanisms.
Commonly temporary filter is placed in abdomen vein (IVC) to prevent dislodgement of clots into pulmonary/Lung veins. IVC filter should be removed after 4 to 6 weeks of placement.
Main indication of IVC filter is failure or contraindication of blood thinners and repeated pulmonary embolism in spite of conservative management.
Book Appointment
-
Varicose Veins & Varicose Ulcer Treatment
-
Non-Healing Wound Management
-
Vascular Malformations
-
Uterine Fibroid or Prostate Embolization
-
Cancer Treatments – TACE, RFA, Embolization
-
Dialysis Access Catherization
-
Diagnostic Procedures – FNAC, Biopsy, Diagnostic Angiography
-
Abscess Treatment - Aspiration, Pigtail Drainage
-
Treatment of Aneurysm and Stroke
-
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
-
Other USG, CT & DSA Guided Interventions
