OTHER USG, CT & DSA GUIDED INTERVENTIONS
Biliary Intervention
Placement of catheters in the biliary system to bypass biliary obstructions and decompress the biliary system.
Placement of permanent indwelling biliary stents.
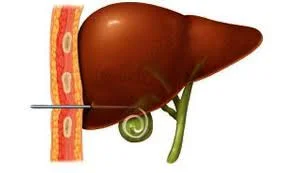
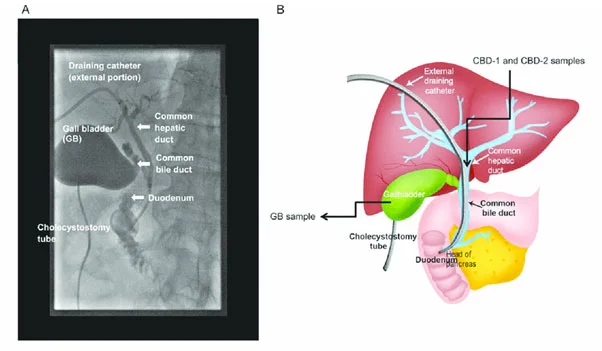
Cholecystostomy: Placement of a tube into the gallbladder to remove infected bile in patients with cholecystitis, an inflammation of the gallbladder, who are too frail or too sick to undergo surgery.

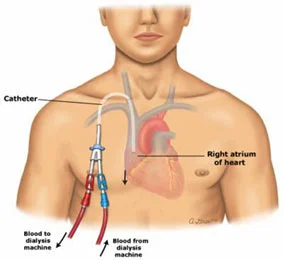
Central Venous Catheter Placement
Vascular access and management of intravenous devices (IVs), including both tunneled and non-tunneled catheters (e.g. PIC, Hickman, port catheters, hemodialysis catheters, translumbar and transhepatic venous lines).

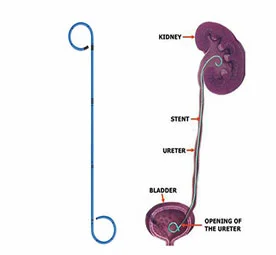
Genitourinary
Percutaneous nephrostomy or nephroureteral stent placement: Placement of a catheter through the skin, directly into the kidney to drain from the collecting system. This is typically done to treat a downstream obstruction of urine.


Ureteral stent exchange: indwelling double-J type ureteral stents, typically placed by urologist using cystoscopy, may be exchanged in retrograde fashion through the female urethra. The IR uses a thin wire snare under fluoroscopy to capture the distal portion of the stent. After partially extracting the distalmost stent, exchange for a new stent can be accomplished over a guidewire.
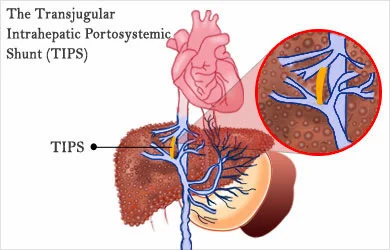
TIPS: Placement of a Transjugular Intrahepatic Porto-systemic Shunt (TIPS) for selected indications in patients with critical end-stage liver disease and portal hypertension.
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) is a procedure that may be used to reduce portal hypertension and its complications, especially variceal bleeding. A TIPS procedure may be done by a radiologist, who places a small wire-mesh coil (stent) into a liver vein. The stent is then expanded using a small inflatable balloon (angioplasty). The stent forms a channel, or shunt, that bypasses the liver. This channel reduces pressure in the portal vein. By reducing portal hypertension, enlarged veins (varices) are less likely to rupture and bleed. And other complications of cirrhosis called ascites (fluid in the abdomen) and hepatic hydrothorax (fluid between the lungs and the chest wall) may improve or go away.

Book Appointment
-
Varicose Veins & Varicose Ulcer Treatment
-
Non-Healing Wound Management
-
Vascular Malformations
-
Uterine Fibroid or Prostate Embolization
-
Cancer Treatments – TACE, RFA, Embolization
-
Dialysis Access Catherization
-
Diagnostic Procedures – FNAC, Biopsy, Diagnostic Angiography
-
Abscess Treatment - Aspiration, Pigtail Drainage
-
Treatment of Aneurysm and Stroke
-
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
-
Other USG, CT & DSA Guided Interventions
